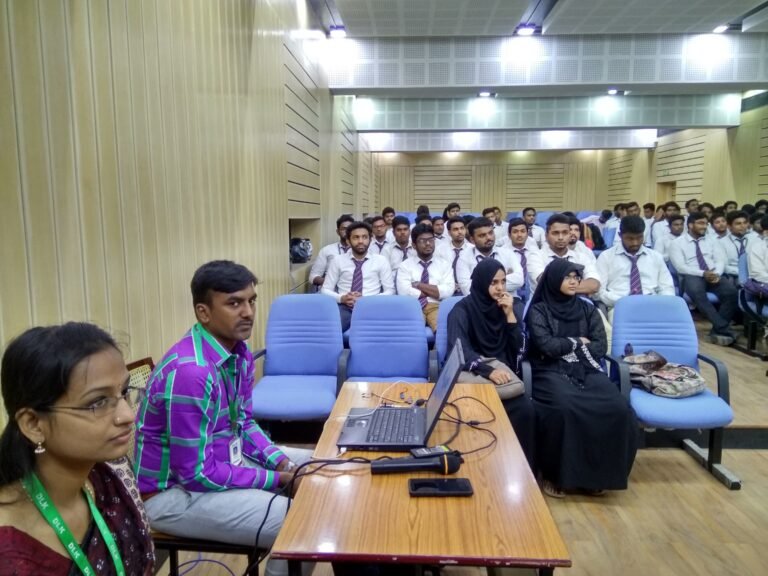
ABOUT EMBEDDED SYSTEM TRAINING
Embedded systems enable learners to make genuine applications. The installed frameworks course is gone for giving fantastic preparation to programming engineers and also the individuals who wish to enter this field.
- Real Time Experts as Trainers
- Certification
- Flexibility
- LIVE Project
- Affordable Fees
- Placement Support
Have Queries? Talk to our Career Counselor for more Guidance on picking the right career for you!
Enquiry Form
About Embedded system Training
Embedded systems enable learners to make genuine applications. The installed frameworks course is gone for giving fantastic preparation to programming engineers and also the individuals who wish to enter this field. In this course, understudies can learn pragmatic lessons and methods used to configuration, actualize, incorporate, and test programming utilized for cutting edge implanted frameworks. The course offers the learners point by point depiction of the life-cycle for planning multi-objective and multi-train installed frameworks.
Our Embedded Systems course focuses on essential level preparing to cut edge level preparing. Our Embedded Systems Training in totally centered to get arrangements in MNC in Chennai and accreditation on Embedded Systems after consummation of our course. Our group of Embedded Systems coaches is Embedded Systems confirmed experts with all the more continuous involvement in live undertakings. Our Embedded Systems Course syllabus is sufficient for any individual who needs to get Embedded Systems affirmation that meets industry desires. In our course arrangement, you will take in installed frameworks from essential to cutting edge level in a viable way.
Embedded system Courses at DLK
DLK Career Development Centre is a highly focused Embedded systems and Embedded C, data science training institute in Chennai. We offer state of art training in Embedded Systems, IOT, Python, device drivers, Embedded linux, ARM, C, C++, RTOS, Robotics, Machine Learning and Automation Testing. Aiming to bridge the space among the demands of the enterprise and the curriculum of educational establishments. Our training methodology is particularly targeted on a hands-on realistic approach with applicable tasks which affords reasonable publicity to diverse phases of software program and application development existence cycle.

Online Training
Instructor LED Live Online Training

Classroom Training
Instructor LED Classroom Training
One to One Training
Customized and Exclusive Training

Team/Corporate Training
Customized Corporate Training
Course Highlights and Why Embedded system in Chennai at DLK?
- Course Timing- All days Monday to Saturday from 10 am to 7 pm.
- Training hours – 48 to 60 hours
- Course – Training in Software installation
- Hardware – We make hardware, and show how is it working.
- Course Documentation, with PPT or PDF, and project report.
- Certificate – After Successful completion of the training, certification will be done by us.
Syllabus
- Embedded C
- Data Types
- variables
- Introduction to C Programming, Variables and Data Types
- Input and Output, Condition Statements
- Functions, Array, String
- Pointer Concept, Structure and Union, File Handling
- Introduction to 8051
- Pin Configuration, LED Interfacing, LCD Interfacing
- Keypad Interfacing, Motor interfacing, Timers, Counters
- ADC, Serial Communication, Interrupts
- Introduction to PIC Microcontroller
- Pin Configuration, LED and LCD Interfacing, Keypad Interfacing
- Motor interfacing, Timers, Counters, ADC
- Serial Communication, SPI, I2C, Interrupts
- Introduction to ATMEGA, Pin Configuration, LED and LCD Interfacing
- Timers, Counters, ADC, Serial Communication, SPI
- Keypad Interfacing
- Motor interfacing
- I2C, MAX 7221, RTC, Interrupts
- Keypad Interfacing
- Motor interfacing
- TimersSection 9: Serial Communication 60 Hrs
- ADC, Serial Communication
- SPI, I2C
- GLCD (Graphical LCD)

Embedded system Certification Training in Chennai.
Trainer Profile
- Our trainers are well versed in technical wise and they are knowledgeable in their professions
- Our trainers will explain the students in a very easy method, such a way the students will understand easily.
- Our trainers will put their maximum effort in explaining the students
- Our trainers have well experienced and put their full effort in explaining during the discussion with the students
- Our trainers will give attention individually to all the student by one on one, until the student get well versed in it.r trainers have well experienced and put their full effort in explaining during the discussion with the students
Course Training Meterial
- We take one to one responsibility to every student
- Study Materials will be given
- Programming code – issued
- Hardware – We Guidelines in Technology – will be explained well.make hardware, and show how is it working.
Course Certificate
- After completion of the training, successfully, the student will be issued a course completion certificate.
Who Can Attend this Programme?
- College students from 1st year to 4th year
- Fresh pass-out students
- Peoples who are searching good jobs
Outcome Of This Training Programme?
- Will be a well-trained Programmer before graduation
- Will be a well-trained Programmer before graduation
- Acceptance of work in all their fields
- To develop good attitude, speedy in their work
- Will get good placements in MNC’s
Section 1: The Fundamentals - Embedded programming and the role of C++
- 1.2.1 TMS 1000
- 1.2.2 Intel MCS-48
- 1.2.3 Intel MCS-51
- 1.2.4 PIC
- 1.2.5 AVR
- 1.2.6 M68k and Z80-based
- 1.2.7 ARM Cortex-M
- 1.2.8 H8 (Super H)
- 1.2.9 ESP8266/ESP32
- 1.2.10 Others
- 1.2.11 Challenges
- 1.3.1 Challenges
1.1 The many faces of embedded systems
1.2 Microcontrollers
1.3 System-on-Chip/Single Board Computer
1.4 Summary
- 2.1 C++ relative to C
- 2.2 C++ as an embedded language
- 2.3 C++ language features
- 2.3.1 Namespaces
- 2.3.2 Strongly typed
- 2.3.4 Type conversions
- 2.3.5 Classes
- 2.3.6 Inheritance
- 2.3.7 Virtual base classes
- 2.3.8 Function in lining
- 2.3.9 Runtime type information
- 2.3.10 Exception handling
- 2.3.11 Templates
- 2.4 The standard template library
- 2.5 Maintainability
- 2.6 Summary
- 3.3.1 Adding an RTC
- 3.3.2 Custom drivers
- Relays
- Debounce
- Debounce HAT
- Power
- Listener
- Club
- HTTP request handler
- Status handler
- Data handler
3.1 Embedded operating systems
3.2 Real-time OSes
3.3 Custom peripherals and drivers
3.4 Resource limitations
3.5 Example – club room monitoring
3.5.1 Hardware
3.5.2 Implementation
3.5.3 Service configuration
3.5.4 Permissions
3.5.5 Final results
3.6 Example – basic media player
3.7 Summary
- 4.1.1 Example – Machine controller for a laser cutter
- 4.4.2 Functional specification
- 4.4.3The design requirements
- 4.4.4 Implementation-related choices
- 4.3.1 Memory programming and device debugging
- 4.3.2 Boot loader
- 4.4.1 Stack and heap
- 4.4.2 Interrupts, ESP8266 IRAM_ATTR
- 4.6.1 Enter Nodate
- 4.6.2 Example – CMOS IC Tester
- 4.6.3 Usage
4.1 The big picture for small systems
4.2 Embedded IDEs and frameworks
4.3 Programming MCUs
4.4 Memory management
4.5 Concurrency
4.6 AVR development with Nodate
4.7 ESP8266 development with Sming
4.8 ARM MCU development
4.9 RTOS usage
4.10 Summary
- Makefile-user.mk
- Main
- OtaCore
- BaseModule
- PlantModule
- Index.html
5.1 Keeping plants happy
5.2 Our solution
5.3 The hardware
5.4 The firmware
5.4.1 Setting up Sming
5.4.2 Plant module code
5.4.3 Compiling and flashing
5.4.4 First-time configuration
5.4.5 Using the system
5.5 Taking it further
5.6 Complications
5.7 Summary
Section 2: Testing, Monitoring
- 6.3.1 Mock versus hardware
6.1 Avoiding real hardware
6.2 Cross-compiling for SBCs
6.3 Integration test for club status service
6.4 Testing with Valgrind
6.5 Multi-target build system
6.6 Remote testing on real hardware
6.7 Summary
- 7.6.1 The server
- Make file
- 7.6.2 The node
- Make file
- 7.6.3 Building the project
7.1 Reducing wear
7.2 Planning out a design
7.3 Platform-independent build systems
7.4 Using cross-compilers
7.5 Local and on-chip debugging
7.6 Example – ESP8266 integration test
7.7 Summary
- 8.1 One box that does everything
- 8.2 Hardware needed
- 8.3 Software requirements
- 8.4 Bluetooth audio sources and sinks
- 8.5 Online streaming
- 8.6 Voice-driven user interface
- 8.7 Usage scenarios
- 8.8 Source code
- 8.9 Building the project
- 8.10 Extending the system
- 8.11 Summary
- CO2 module
- Jura
- JuraTerm
- Motion
- PWM
- I/O
- Switch
9.1 Plants, rooms, and beyond
9.2 Developmental history
9.3 Functional modules
9.4 Firmware source
9.4.1 Core
9.4.2 Modules
9.5 Command and control server
9.6 Administration tool
9.7 Air-conditioning service
9.8 Influx DB for recording sensor readings
9.9 Security aspects
9.10 Future developments
9.11 Summary
Section 3: Integration with other tools and frameworks
- 10.8.1 Main
- 10.8.2 QmlInterface
- 10.8.3 QML
10.1 The power of the right framework
10.2 Qt for command-line use
10.3 GUI-based Qt applications
10.4 Embedded Qt
10.5 Custom GUIs with stylesheets
10.6 QML
10.7 3D designer
10.8 An example of adding a GUI to the infotainment system
10.9 Summary
- 11.5.1 The hardware
- 11.5.2 The VHDL code
- 11.5.3 The C++ code
11.1 Going extremely parallel
11.2 Hardware description languages
11.3 FPGA architecture
11.4 Hybrid FPGA/SoC chips
11.5 Example – basic oscilloscope
11.6 Building the project
11.7 Summary
Best Practices
- i. All the best-laid plans
- ii. Working with the hardware
- iii. The confusing world of peripherals
- iv. Knowing your tools
- v. Choosing asynchronous methods
- vi. Reading the datasheet
- vii. Keeping interrupt handlers short
- viii. 8-bit means 8 bits
- ix. Don't reinvent the wheel
- x. Think before you optimize
- xi. Requirements are not optional
- xii. Documentation saves lives
- xiii. Testing code means trying to destroy it
- xiv. Summary


